
11
2020


Abstract:
In the sol–gel science, the influence of chemical aging on the fundamental water permeability remains open regarding to the durability performance of cement-based material. To reveal the pure effect of chemical aging, the water permeability and related micro-structural characteristics are measured on water-saturated mature mortars, whose aging is accelerated through heat treatment under water. It is found that, the chemical aging increases the volumetric porosity and coarsens the pore structure to a notable extent, which enlarge water permeability by 2.6–4.9 times. Based on the pore structure obtained through the low-field proton NMR technique, the water permeability is predicted by the Katz–Thompson theory with satisfactory accuracy, quantitatively confirming the direct effects of chemical aging on water permeability. Physically, because of the polymerization and rearrangement of C–S–H gel, cement mortars undergo substantial changes with enlarging radii for both interlayer and gel pores, slightly decreasing interlayer space but remarkably enlarging gel pore space.
Keywords:
Mortar; Calcium-silicate-hydrate ;Chemical aging ;Water permeability ;Pore structure ;
11
2020


Abstract and Figures
05
2020


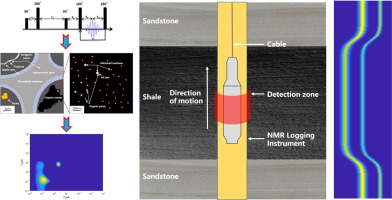
Inside-out nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a unique technique for investigating large in-situ objects outside of tools, to provide pore structure and pore-bearing fluids properties. However, in borehole, objects towards azimuthal orientations pose different properties, referred to as azimuthal spatial heterogeneity. This may lead to ambiguous evaluations by utilizing present inside-out NMR measurement, which hardly resolves azimuthal information and loses the location information of oil/gas. In this paper, we for the first time design and construct an innovative tool to investigate the heterogeneity of large in-situ samples. The most key component, array coil, which performs with azimuthal selection, measurement consistency and interactive isolation, configured in this novel tool to capture heterogeneity information. Whereas, strong coupling between neighboring coil elements largely decrease the coil sensitivity. Capacitive decoupling network is bridged into adjacent ports without segmenting coils to be decoupled and could be easily adjusted by electrical relays. The coil model and numerical simulation are firstly given to demonstrate the array coil configuration, B1 field map and mutual coupling effects on coil sensitivity. Capacitive network is then introduced to be theoretically and practically analyzed to minimize coupling effects. Simulation and experimental results demonstrate that these coil elements have excellent consistency and independence to feasibly acquire the azimuthal NMR data.

摘要:为深入揭示水泥基材料渗透率与孔结构间的关系,以不同水灰比、不同温度水养的白水泥砂浆为研究对象,利用低场磁共振与压汞技术分别测试了砂浆在饱水与干燥状态下的孔径分布,并利用稳态渗透法测试其水分渗透率。结果表明:砂浆在饱水与干燥状态下的孔结构差异显著,临界孔径相差1 个数量级左右,原因在于水化硅胶钙(C-S-H)凝胶具有显著的水敏性。经历56 d 80 ℃热水养护后,由于C-S-H 凝胶高温老化加速,饱水砂浆的孔隙率及临界孔径显著增大,孔结构明显粗化,水分渗透率增大,对耐久性不利。干燥预处理对压汞测试所得孔结构的影响可能远超高温老化,在分析孔结构变化时必须考虑水敏性的影响,否则可能得出错误结论。将孔隙视作不同大小的毛细管束,经典Kozeny-Carman 模型可基于低场磁共振测试所得饱水孔径分布曲线来准确预测水分渗透率,将比例系数取为1.09 所得理论值与实测值的相对误差在[–42.7%, 71.1%]范围内,预测精度接近极低渗透率测试的误差水平。

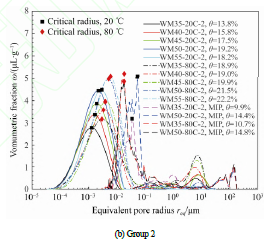
关键词:水泥砂浆;水分渗透率;孔结构;低场磁共振;水敏性;
摘要:针对目前油气田现场广泛采用的多相流分离检测技术存在的效率低、精度差、数据延迟等问题,研究基于磁共振技术的多相流在线检测方法,形成硬件装置,并开展室内实验及现场应用。提出“静止状态测相含率+流动状态测流速”的多相流磁共振流量测量方法;提出先计量油水比再计量含气率的方法实现油、气、水三相相含率的测量。在装置研制方面,提出可应用于流动流体测量的分段式磁体结构和双天线结构,研发了高集成磁共振谱仪系统及配套智能化软件。室内实验及现场应用表明,研制的多相流磁共振在线检测系统存在以下优势:只依靠磁共振技术同时完成流量和相含率检测;在线原位高频率检测,实时监测油井瞬态产液波动;能实现油、气、水三相全量程高精度检测,且不受矿化度、乳化状态影响;绿色、安全、低能耗。
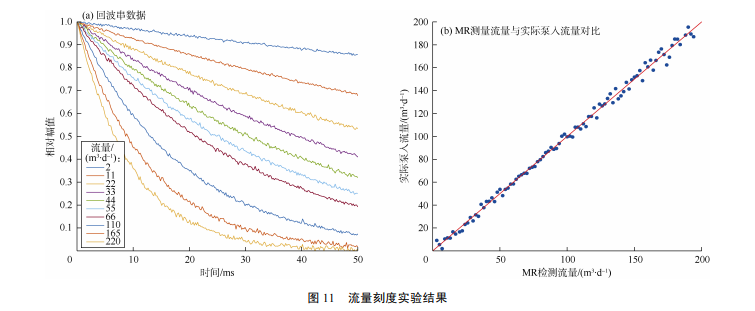
关键词:多相流;磁共振;流量;相含率;检测方法;检测装置
03
2020


Abstract:
Tuff rock is highly heterogeneous due to volcanic activity, hydrothermal alteration, and weathering. It is difficult
to explain the deterioration mechanisms of the weathered rocks merely based on mineralogical and chemical
parameters. It has been reported that subtle weathering can modify pore structure and subsequently affect the
rock mechanical behavior of tuffs. In this work, the pore characteristics in slightly weathered tuffs and fresh tuffs are systematically analyzed based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) tests. Additionally, meso-level uniaxial compression tests were conducted on the tuff samples by utilizing the MTI–LM (miniature tensile instrument–light microscope) system to detect the crack propagation and deformation process. The results demonstrated that additional mesopore (10–50 nm) increases with pore throat expansion during weathering, and the change of pore structure influences the tuff failure mode. Specifically, for the slightly weathered tuff, crack initiates in the altered minerals or matrix and results in shear failure. However, as for the fresh tuff, crack usually initiates in the intact and fresh minerals and matrix, and eventually leads to tensile failure. Therefore, we propose that tuff pore property can serve as potential indicator of the micromechanism of substantial macro-deterioration due to weathering.
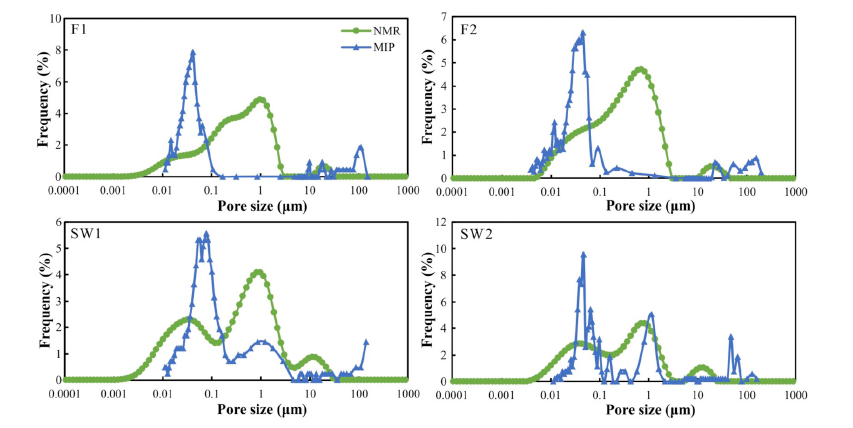
Keywords:
Tuff, Weathering, Pore structure, Macro-deterioration;
11
2019


bstract:
Low field two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (2D-NMR) relaxometry is a powerful probe for the characterization of heterogenous, porous media and provides geometrical, physical and chemical information about samples at a molecular level and has been widely used in shale studies. However, NMR signals of shale decay so rapidly, dry sample for particular, that the conventional two-dimensional pulse sequence is either not sensitive enough to short relaxation components or takes too much measurement time. In this paper, 2D-NMR relaxometry correlation based on partial inversion recovery CPMG (PIR-CPMG) pulse sequence is proposed and illustrated to improve the contrast over saturation recovery CPMG (SR-CPMG) and reduces the T1 encoding time of inversion recovery CPMG (IR-CPMG) for petrophysical characterization of shale. Subsequently, the kernel function and inversion method of the proposed pulse sequence is presented and the reliability of the inversion method is testified by numerical simulation. Next, theoretical analysis is conducted to validate the advantages of the proposed pulse sequence. Ultimately, experiments on copper sulfate solution, artificial sandstone and shale samples are performed, respectively, to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed pulse sequence. The results demonstrate that the PIR-CPMG sequence possesses the advantages of time saving and high contrast, especially for the short relaxation components. The proposed pulse sequence can be utilized in bench-top NMR core analyzer and downhole well logging, potentially, to achieve integrated petrophysical characterization of shale.
Keywords:Low field NMR, Two-dimensional relaxometry, Pulse sequence, Shale
11
2019


Abstract:
Low field nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry (LF-NMR) was used to study the setting process of alkali-activated GGBFS (AA-GGBFS) paste during the early curing hours. LF-NMR measurements were carried out from fresh paste casting until hardening (generally no more than 8 h). The transverse relaxation time T2 was used as a probe to assess the setting process. Combined with Vicat penetration and temperature monitoring, an important threshold indicator was defined as the deadline for paste casting (DPC). The physical meaning of the DPC is a threshold point where the developing micro pores make loss of movable water attain a certain level so that the semi-solid paste has slight strength. Moreover, several periods related to AA-GGBFS early-hour paste development are proposed: (1) dissolution; (2) setting; (3) acceleration; and (4) hardening. By analysing each period during the early hours, it was found that the hybrid retarder of zinc nitrate and sodium gluconate works for the AA-GGBFS system.
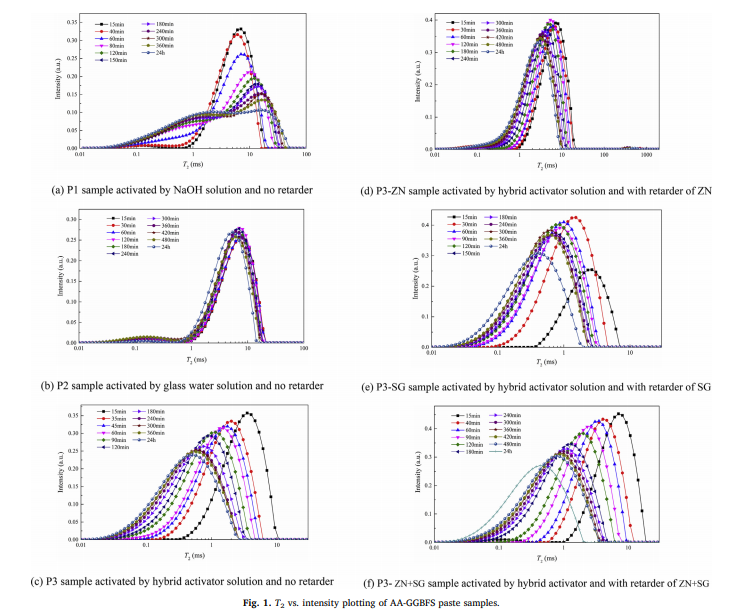
Keywords:
NMR relaxometry ,Alkali-activated GGBFS, Setting time, Chemical reaction, Retarders;
05
2019


Abstract:
Influence of wettability to petrophysical responses in low permeability reservoirs is increasingly evident, but research of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology on wettability calibration in such reservoirs is very limited even though it has been used promisingly. The challenge is that the empirical interpretation model only applies to simple pore structure. It is urgent to develop a relatively simple, quick, and practicable model for wettability evaluation in low permeable reservoirs.
This paper presents an experimental NMR study, integrating with Amott tests, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) measurements, on wettability characterization of five typical core samples from different low-permeability reservoirs. NMR relaxation mechanisms and the effect of the aging were analyzed in detail. The study showed that all the core samples had a shift of T2 (spin-spin relaxation time) spectra between before and after aging. According to the shift characteristics, the core samples were divided into two types. The first type is that the wettability alteration relied on the aging and it displaced crude oil into original water-wet movable pore spaces to restore reservoir wettability. This type of formation is generated in distant-source reservoirs, which mainly involves fluid transport through buoyancy. Another type is that the wettability alteration was attributed to the natural oil-wet property of the rock matrix. This formation is mainly found in inner-source or near-source reservoirs, which may generate abundant oil-wet materials. Thus, the wettability alteration is the result of hydrocarbon accumulation modes. Based on the observations, a potential method for obtaining the wettability index was proposed. The method uses both the ratio of oil-wetted to water-wetted pore surface areas and diffusion-relaxation diagrams. The estimated results corresponded reasonably to the independent Amott tests. This study demonstrates that NMR relaxation is an effective solution to analyz
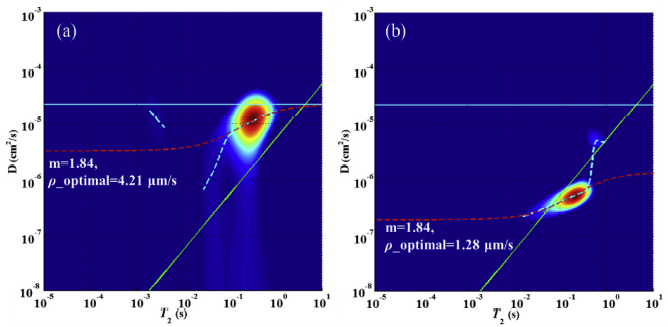
Keywords: Wettability,NMR relaxation,Low-permeability reservoir,Aging,Reservoir type
10
2019


Abstract:
The main concern of this article is to understand the influences of red mud on the properties of magnesium phosphate cement (MPC), which were determined in terms of the fluidity, setting characteristic, temperature evolution during the hardening stage, mechanical properties, water resistance, hydration products, pore structure and microstructure. The results showed that the fluidity can increase to a value of 272.5 mmat a level of 20% red mud, and red mud was found to decrease the exothermic reaction intensity of the fresh mortar and to prolong the setting time to 25 min during the hardening stage. The mortar prepared with suitable addition of red mud presented with improved mechanical properties and enhanced water resistance during the whole ageing period, and the group containing 20% red mud yielded the highest compressive strength of 90.2 MPa at 28 days. Then, the pore structure was measured by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR), which was found that adding red mud can reduce the total porosity and form more small pores. Moreover, the microstructure and the hydration products of the samples were tested by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) along with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). The obtained results illustrated that red mud can fill in the microcracks, making the structure denser, and also formed with some new hydrates. The present work aimed at the utilization of red mud and the results illustrated that MPC can be modified by red mud significantly.
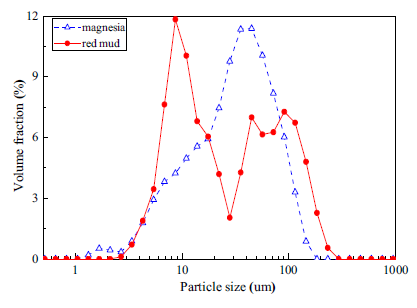
Keywords: Red mud, Magnesium phosphate cement, Water resistance, Microstructure, Hydration products
01
2019


Digital Rock Physics(DRP)is widely used to accurately characterize pore structures and mineral distributions of hydrocarbon bearing rocks based on their three-dimensional(3D)images at micro-and nano-meter scales.It also plays an important role to numerically calculate rock elasticity,formation factor,permeability and simulate multi-phase flow properties etc.However,3D images are not always readily available for reservoir rocks and it is sometimes difficult to satisfy modeling requirements to cover heterogeneity due to limited rock volumes captured in 3D.Therefore,3D reconstruction methods become alternative approaches to model porous rocks.Comparing with statistical methods,geological process based reconstruction hasproved itself to be successful to reproduce sandstone structures.In this paper,we developed a method to improve the existing models with more realistic sedimentological processes and extend it to reconstruct shaly sandstone,carbonate rocks and shale by introducing more mechanism of diagenesis.The grain size distribution is extracted from a slice of 2D Micro-CT images using watershed segmentation algorithm;and then it is used as initial input information for the 3D reconstruction.The accuracy of modeling is evaluated by comparing their local porosity distributions and average percolation probability function distributions of the 3D digital rock images obtained by MicroCT imaging.The results show that our reconstruction can accurately reproduce heterogeneity and percolation characteristics of original Micro-CT images,which provide geologically realistic rock models for petrophysical studies.
05
2019


Abstract:
Permeability characterizes how saturating fluids penetrate and flow through porous rocks. It is an important quantity that can be used to model the behavior of reservoir rocks and to optimize underground resource exploration. Permeability can be characterized via nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) relaxometry techniques by utilizing the yielded pore volume and pore length scales. However, for heterogeneous rocks a simple estimation of a permeability value based on the existing models may be inadequate. In this work, a new relaxation technique is applied to rock cores in conjunction with magnetic resonance imaging schemes. This allows the interior structures of studied rock cores to be recorded along a chosen sample axis. Based on the spatially resolved relaxation maps obtained, a factor of local connectivity was introduced for the first time and calculated by using the correlation degree between adjacent relaxation time distributions originating from neighboring image slices. Consequently, a permeability profile was estimated by consecutively considering the local porosity, the spatially resolved relaxation time distribution, and the connectivity factor. Experimental results prove that permeability profiles trace the heterogeneity of rock samples. Furthermore, averaged permeabilities of rock cores were calculated while taking into account local connectivity. The values obtained approach better to brine‐permeability measurements as compared to data processing disregarding connectivity.
Keywords: Rock cores, Permeability, Low‐field NMR
10
2019


Abstract:
In the petroleum industry, detection of multi-phase fluid flow is very important in both surface and down-hole measurements. Accurate measurement of high rate of water or gas multi-phase flow has always been an academic and industrial focus. NMR is an efficient and accurate technique for the detection of fluids; it is widely used in the determination of fluid compositions and properties. This paper is aimed to quantitatively detect multi-phase flow in oil and gas wells and pipelines and to propose an innovative method for online nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) detection. The online NMR data acquisition, processing and interpretation methods are proposed to fill the blank of traditional methods. A full-bore straight tube design without pressure drop, a Halbach magnet structure design with zero magnetic leakage outside the probe, a separate antenna structure design without flowing effects on NMR measurement and automatic control technology will achieve unattended operation. Through the innovation of this work, the application of NMR for the real-time and quantitative detection of multi-phase flow in oil and gas wells and pipelines can be implemented.
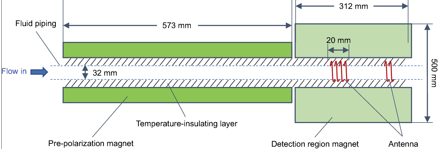
Keywords:Oil and gas wells, Multi-phase flow, NMR, Online detection
11
2018


Abstract:
Currently, commercial downhole nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) tools can measure depth (along with borehole axis) and radial (perpendicular with borehole axis) profile information simultaneously. However, in many cases, the lack of information due to the strong heterogeneity, partial invasion of the drilling mud around the borehole or borehole collapse will have a serious impact on applications. In order to ensure the validity of each measurement, acquisition of azimuthal information is as important as the depth and radial profile information. In this paper, we described the performance and response simulation of an innovative centralized downhole NMR scanning probe (SMRT). This probe uses hollow cylinder magnets as main magnets to produce azimuthally symmetrical polarized (related to the z-axis) static magnetic field B 0 . Circular focusing magnets and high permeability materials are added between the main magnets to simultaneously adjust the field homogeneity along with z-axis, increase the height of sensitive region and enhance the strength of B 0 field in sensitive region. Coil array is composed of eight independent coil units with the same performance but different azimuthal selection function used to scan the formation around the probe so that eight azimuthally distinguishable sensitive regions can be investigated. Magnets and coil array configuration are optimized with the finite-element method, and B 0 field and B 1 field is calculated to obtain the spin dynamic response. Numerical simulation results show that NMR signals from different azimuthal sections had no overlapped feature (sensitive volume of each azimuthal direction is thin shell of arc length approximate 45°) and high azimuthal resolution is feasible.
Keywords:IEEE Keywords, Nuclear magnetic resonance, Probes, Tools, Mathematical model, Petroleum, Numerical models
11
2018


Abstract:
Currently, commercial downhole nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) tools can measure depth (along with borehole axis) and radial (perpendicular with borehole axis) profile information simultaneously. However, in many cases, the lack of information due to the strong heterogeneity, partial invasion of the drilling mud around the borehole or borehole collapse will have a serious impact on applications. In order to ensure the validity of each measurement, acquisition of azimuthal information is as important as the depth and radial profile information. In this paper, we described the performance and response simulation of an innovative centralized downhole NMR scanning probe (SMRT). This probe uses hollow cylinder magnets as main magnets to produce azimuthally symmetrical polarized (related to the z-axis) static magnetic field B 0 . Circular focusing magnets and high permeability materials are added between the main magnets to simultaneously adjust the field homogeneity along with z-axis, increase the height of sensitive region and enhance the strength of B 0 field in sensitive region. Coil array is composed of eight independent coil units with the same performance but different azimuthal selection function used to scan the formation around the probe so that eight azimuthally distinguishable sensitive regions can be investigated. Magnets and coil array configuration are optimized with the finite-element method, and B 0 field and B 1 field is calculated to obtain the spin dynamic response. Numerical simulation results show that NMR signals from different azimuthal sections had no overlapped feature (sensitive volume of each azimuthal direction is thin shell of arc length approximate 45°) and high azimuthal resolution is feasible.
Keywords:IEEE Keywords, Nuclear magnetic resonance, Probes, Tools, Mathematical model, Petroleum, Numerical models
04
2018


Abstract
Two 2D-NMR methods were introduced for characterizing the heterogeneity of rock plugs with different lithologies. The first one, so-called eigenmode correlation experiment, allows one to obtain pore length scales correlated to NMR relaxation time, and to intrinsically extract surface relaxivity values from 2D eigenmode correlation maps. The second approach couples the pore length scales with solid-liquid magnetic susceptibility contrast Δχ. NMR results from these two methods are compared and confirmed with independent SEM and micro-CT measurements. It demonstrates that both methods are capable to indicate the heterogeneity degree and do not require sophisticated NMR pulse sequence, which facilitates their implementations in NMR systems on porous rock research.
Graphical abstract

11
2018


Abstract:
During last 20 years, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) fluid analyzer is becoming a usual instrument to conduct researches to fluids several thousand meters underground in real time due to its nondestructive, rapid, and repeatable characteristics. In this paper, a new set of down-hole NMR fluid analyzer was designed and implemented. The probe of the analyzer employs special ring-shaped magnets which can be fastened to a high permeability material with a card slot. This design can decrease the twist between adjacent magnet blocks and obtain a homogeneous magnetic field. Meanwhile, in the axis direction, a stabilization section was added to the polarized magnets for improving the polarization efficiency. Furthermore, the system adopts a multiple antenna structure, by which it can achieve multi-parameter and multi-function measurements. To match with the antenna structure, an antenna control module was put to the circuit system to quickly switch the working antenna. Then, the performance of this new designed system was validated by both stationary and flow fluid. In the future, the analyzer can be combined with the formation tester for down-hole fluid analysis or used independently for ground fluid analysis during oil exploitation and transportation.
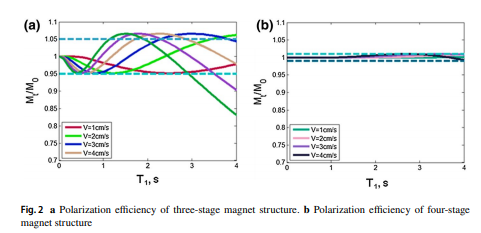
Keywords:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR);
10
2018


Abstract:
In low-field NMR, depth information and radial profile information of downhole formation can be easily acquired with the help of static gradient magnetic field produced by permanent magnets, called downhole NMR imaging. Based on the hypothesis that the formation is homogeneous, average signals detected by centralized or decentralized sensors can provide enough information for petrophysical parameters. In fact, the inhomogeneity of formation may have serious impact on description of the characteristics of formation and oil/gas location which is rarely studied in NMR well-logging. To improve this, we design and implement a new quadrupolar magnet array aimed at achieving azimuthal measurement in this paper. A new quadrupolar magnet array is consisted of four bread-shaped magnets combined with additional small hexangular magnets to produce enough strength and high homogeneity of static field along with circumferential direction at deeper DOI (depth of investigation). Azimuthal measurements are achieved by using coil array combined with quadrupolar magnet array.
Keywords: Azimuthal measurement, Downhole NMR, Magnet array
10
2018


Abstract:
NMR spin-lattice (T1) and spin-spin (T2) relaxation times and their inter-relation possess information on fluid behaviour in porous media. To elicit this information we utilize the pseudo 2-D relaxation model (P2DRM), which deduces the T1–T2 functional relationship from independent 1-D T1 and T2 measurements. Through model simulations we show empirically that the P2DRM accurately estimates T1–T2 relationships even when the marginal distributions of the true joint T1–T2 distribution are unknown or cannot be modeled. Estimates of the T1:T2 ratio for fluid interacting with pore surfaces remain robust when the P2DRM is applied to simulations of rapidly acquired data. Therefore, the P2DRM can be useful in situations where experimental time is limited.

Keywords: Relaxation, correlation, Lognormal distributionInverse-gamma distribution, Magnetic resonance in porous media, Heterogeneity, Multidimensional distribution function
08
2018


Abstract:
Reservoir properties, such as pore types and wettability, are essential for shale gas reservoir evaluation. However, advanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), which has been routinely used in petrophysical characterization of reservoirs, is barely used to estimate these properties in shale gas reservoirs. In this study, several sets of specially designed NMR measurements, together with total organic carbon (TOC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and contact angle tests, are used to study the pore types and wettability of Longmaxi shale gas reservoir. Results show that the NMR transversal relaxation time (T2) spectrum can be used to characterize pore types and wettability of gas shale. Three identified T2 spectral peaks (0.01–0.4 ms, 0.4–15 ms, and >15 ms) separately correspond to organic pores, inorganic pores, and microfractures, which is consistent with the results of FE-SEM. The T2 spectra in as-received and water/oil-imbibition states qualitatively prove that the microwettabilities of organic pores, inorganic pores, and microfractures are oil-wet, water-wet, and mixed-wet, respectively. In addition, a novel wettability index is defined to reflect the microwettability of pores quantitatively. The dominant minerals and TOC jointly affect the pore wettability index; they show good correlations with the wettability index of inorganic and organic pores, whereas there is no obvious correlation with the wettability index of microfracture. In contact angle measurements, water and oil droplets show different behaviors on the surface of shale specimens, which qualitatively indicates that the macrowettability of Longmaxi gas shale is mixed-wet (both water-wet and oil-wet) and more prone to be oil-wet. After analysis of the theory of characterizing macrowettability by NMR, a new NMR-based model is proposed to characterize the macrowettability quantitatively. In summary, this study proposes novel methods and models to characterize the pore types and wettability, exp
06
2018


Abstract:
Two 2D-NMR methods were introduced for characterizing the heterogeneity of rock plugs with different lithologies. The first one, so-called eigenmode correlation experiment, allows one to obtain pore length scales correlated to NMR relaxation time, and to intrinsically extract surface relaxivity values from 2D eigenmode correlation maps. The second approach couples the pore length scales with solid-liquid magnetic susceptibility contrast Δχ. NMR results from these two methods are compared and confirmed with independent SEM and micro-CT measurements. It demonstrates that both methods are capable to indicate the heterogeneity degree and do not require sophisticated NMR pulse sequence, which facilitates their implementations in NMR systems on porous rock research.
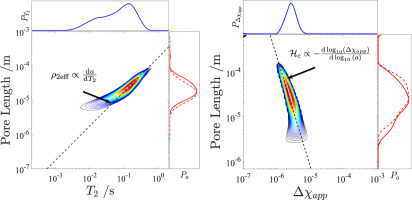
06
2018


Abstract:
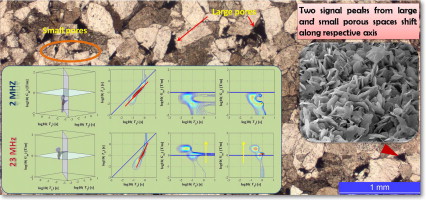
Pore structure is the most important factor affecting reservoir quality and petrophysical property of tight reservoir. The effective characterization of pore structures, including pore radius distribution (PRD), throat radius distribution (TRD), pore-throat radius distribution (PTRD), relevant pore structure parameters, etc., is of great importance for the oil exploration and exploitation. Taking the tight sandy conglomerate reservoir as research target of tight reservoir, this paper characterizes the pore structures by a combination of experiments on parallel core samples. These experiments include high-pressure mercury injection (HPMI), constant-rate mercury injection (CRMI), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), as well as microscopic analysis of casting thin sections and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). This paper systematically analyzes the advantages and shortcomings of these commonly used experimental techniques. And then, novel methods are proposed to characterize the pore structure (especially the full-range PRD, TRD, and PTRD) by utilizing the advantages of these techniques. In addition, an advanced pore classification scheme is proposed to reclassify the pore types. Finally, the controls of the pore structure on the flow characteristics are investigated, which in turn further demonstrates the correctness and importance of the proposed novel methods for characterizing pore structures. In summary, this study proposes novel methods to characterize the pore structure by integration of HPMI, CRMI, and NMR and provides insights into the pore structure characteristics of the tight sandy conglomerate reservoir.
03
2018


Abstract:
The dynamic pore structure of partially saturated cement-based material is rather essential to quantify its mass
transport and many other properties. To clarify the influence of water removal and re-entry, the low-field nuclear
magnetic resonance technique is employed to characterize the pore structure of two white cement mortars during isopropanol exchange and water vapor adsorption kinetics. It is found that, after isopropanol replacement the pore structures of mortars become remarkably coarsen due to the significant collapse of C-S-H interlayer pores, which are only partly reversible at water re-saturation. Consistently, water vapor adsorption is not a simple progressively filling process from finer to coarser pores, but accompanied by continuous expansion of C-S-H gel adsorbing water in priority. Furthermore, the irrecoverable contraction of C-S-H gel is the physical root of irreversible shrinkage. The smaller BET surface area using nitrogen than water is also attributed to the collapse of interlayer pores after drying.
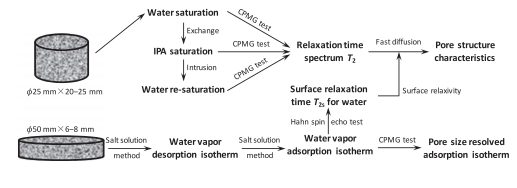
Keywords:
Mortar, Calcium-silicate-hydrate ,Pore structure ,Adsorption, Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LFNMR);
12
2017


Abstract:
Purpose Reduced bone strength is associated with a loss of bone mass, usually evaluated by dual‐energy X‐ray absorptiometry, although it is known that the bone microstructure also affects the bone strength. Here, a method is proposed to measure (in laboratory) the bone volume–to–total volume ratio by single‐sided NMR scanners, which is related to the microstructure of the trabecular bone.
Methods Three single‐sided scanners were used on animal bone samples. These low‐field, mobile, low‐cost devices are able to detect the NMR signal, regardless of the sample sizes, without the use of ionizing radiations, with the further advantage of signal localization offered by their intrinsic magnetic field gradients.
Results The performance of the different single‐sided scanners have been discussed. The results have been compared with bone volume–to–total volume ratio by micro CT and MRI, obtaining consistent values.
Conclusions Our results demonstrate the feasibility of the method for laboratory analyses, which are useful for measurements like porosity on bone specimens. This can be considered as the first step to develop an NMR method based on the use of a mobile single‐sided device, for the diagnosis of osteoporosis, through the acquisition of the signal from the appendicular skeleton, allowing for low‐cost, wide screening campaigns. Magn Reson Med 79:501–510, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: single‐sided NMR, portable NMR, BV/TV, osteoporosis, screening campaigns
摘要:
以万里长城为代表的古建筑是世界瑰宝,更是中华民族的象征和骄傲.本文提出利用便携式核磁共振(NMR)装置来探测研究这类古建筑的建筑材料,在不对其造成损伤的基础上,发掘其隐含的科学、技术和工程相关的丰富信息.为此,作为第一步,设计了适合于探测这类古建筑的便携式单边NMR探测器组合式磁体.该探测器的磁体结构以semi-Halbach为基础,通过不同磁体模块间的组合得到对应移动探测模式、长距离探测模式和均匀磁场探测模式的磁体结构.随后根据优化结果,设计加工了磁体组件,并采用该磁体进行了流体、长城城砖和现代红砖的NMR实验,实测结果与模拟一致.该组合式磁体的优点在于通过不同磁体模块组合,实现了多种探测方式,适用于探测长城等这类古建筑物需要多种探测模式的科学研究.
关键词: 核磁共振(NMR), 单边, 磁体, 磁场
10
2017


Abstract:
The intrinsic permeability of porous medium is theoretically independent of percolating fluids. While concerning cementitious material, its water permeability is anomalously lower than that to many other fluids. To discover the responsible physical background, the permeability coefficients of two mature white cement mortars are measured using water, isopropanol and nitrogen gas. Their pore structures are also tested on specimens at various states through low-field NMR and MIP methods. It is found that the pore structures of water-saturated mortars are remarkably coarsen due to the contraction of C-S-H gel enforced by water removal through drying or isopropanol exchange. The coarsening of pore structure fundamentally increases the intrinsic permeability by 2–4 orders of magnitudes, which can be approximately quantified through the Katz-Thompson equation. The anomalous low water permeability is physically rooted in the swelling of C-S-H gel specific to water, which is intimately linked to the disjoining pressure of aqueous pore solution.
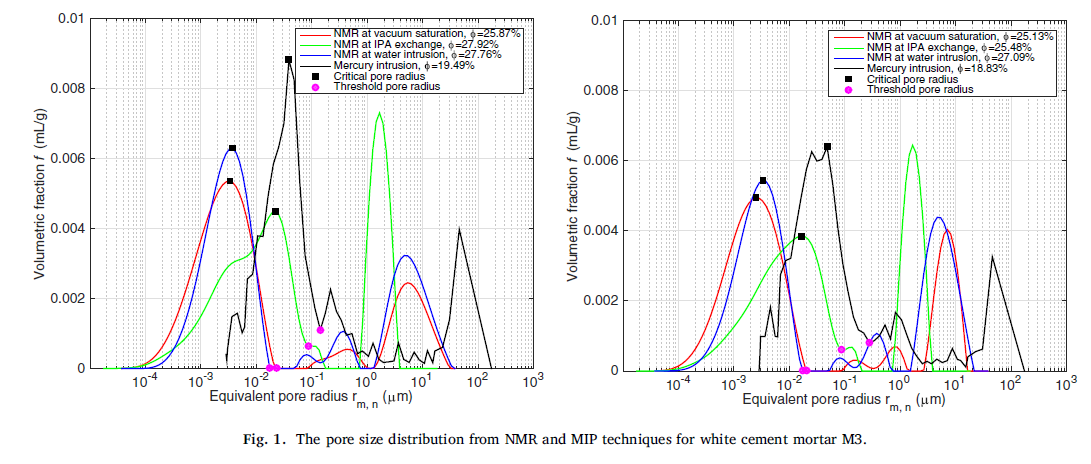
Keywords: Permeability, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP), Pore Size Distribution (PSD), Threshold Diameter;
10
2018


Abstract:
We present a new single-sided NMR sensor which is designed with three detection modes. By combining different modules, this sensor can achieve magnet mode for mobile measurement, large detection depth measurement and “homogeneous” field measurement. The magnets of mobile mode are about 8.6 kg, and its field gradient is about 3.25 T/m. The magnets of large detection depth mode can be obtained by combining the magnets of mobile mode with additional magnets. This mode creates a similar magnetic field as mobile mode, but larger intensity, field gradient and volume of useful region. The “homogeneous” field mode is accomplished by a magnet structure gain from a group of outer magnets combined with a bar magnet. We have demonstrated that this modular and multifunctional single-sided NMR sensor is highly sensitive and is capable to determine relaxation time and diffusion coefficients of different fluids. Such a design is especially suitable for experiments that need to measure many samples in different situations.
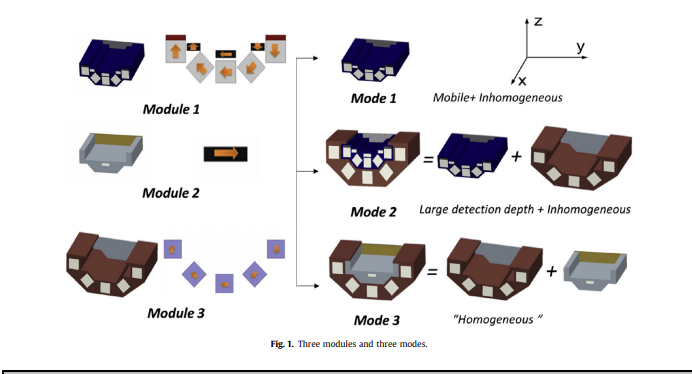
Keywords:
Single-sided NMR ,Modular Design , Multi-Functional;
08
2015


Abstract:
The properties of fluids saturating rocks depend strongly on temperature and pressure. Therefore, ambient laboratory conditions may not be desirable for the investigation of fluids in reservoir rocks. To mimic the reservoir, a pressurized and temperature controlled (overburden) cell, compatible with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), was assembled within a 2 MHz NMR Rock Core Analyzer. 1D NMR relaxation and 2D diffusion-relaxation correlation distributions of fluid-saturated rock cores were measured in conjunction with 1D NMR imaging. By performing these spatially resolved NMR relaxometry and diffusometry experiments within the environment of the overburden cell, it is possible to obtain porosity, fluid saturation and residual fluid content profiles under reservoir-like conditions. Here we show for the first time that these spatially resolved NMR relaxometry and diffusometry experiments could be performed under elevated pressures and temperatures for fluids flooding rock cores in the laboratory. Experiments performed with this NMR setup may allow one to study the oil properties under reservoir conditions, which may inform oil recovery enhancement strategies.
06
2015


Abstract:
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) has been widely employed in the petroleum industry, as oil and gas reservoirs are typical complex porous media. Down-hole NMR measurements (thousands of meters below the surface) face the challenges of high temperature, high pressure, strictly limited size of instruments and high speed tool movement. All these challenges make the probe design, spectrometer manufacture, data acquisition, data processing and interpretation quite different from desktop NMR measurements in the laboratory. In this paper, we present our recent development on the key technologies and implementation of an NMR system for down-hole porous rock applications. The techniques used in developing the down-hole NMR tool have not only been used in oil and gas exploration, but also can be adapted to physics, chemistry, materials, agricultural, food science non-destructive analysis.
Keywords:NMR, Down-hole, Porous rock, Petrophysics, Formation evaluation
01
2015


Abstract:
This paper introduces an innovative methodology for estimating the ageing of asphalt concrete cores without extracting the binder. Asphalt concrete samples at different ageing stages (unaged, 3-month and 6-month aged) and with different percent air voids (4%, 7% and 10%) were analysed with low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The transverse relaxation time T2 and relative hydrogen index (RHI) obtained from NMR measurements were related to the viscosity of the asphalt binder. The samples were analysed during cooling from 70℃ to room temperature, showing increase in viscosity with decreasing temperature. There was a clear trend indicating higher viscosities in samples that were aged for a longer period and samples with higher percent air voids. The RHI and T2 values obtained from low-field NMR measurements and the viscosity data calculated from measurements using a dynamic shear rheometer were correlated to develop a model that relates viscosity with RHI.
Key words: Asphalt,Nuclear Magnetic Resonance,Viscosity,Ageing, T2, Relative Hydrogen Index,Dynamic Shear rheometer;
10
2014


Abstract:
The rapid prediction of fluid viscosity, especially the fluid in heavy-oil petroleum reservoirs, is of great importance for oil exploration and transportation. We suggest a new method for rapid prediction of fluid viscosity using two-dimensional (2D) NMR relaxation time distributions. DEFIR, Driven-Equilibrium Fast-Inversion Recovery, a new pulse sequence for rapid measurement of 2D relaxation times, is proposed. The 2D relation between the ratio of transverse relaxation time to longitudinal relaxation time (T1/T2) and T1 distribution of fluid are obtained by means of DEFIR with only two one-dimensional measurements. The measurement speed of DEFIR pulse sequence over 2 times as fast as that of the traditional 2D method. Using Bloembergen theory, the relation between the distributions and fluid viscosity is found. Precise method for viscosity prediction is then established. Finally, we apply this method to a down-hole NMR fluid analysis system and realized on-site and on-line prediction of viscosity for formation fluids. The results demonstrated that the new method for viscosity prediction is efficient and accurate.
Keywords: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), Two-dimensional measurements, Fluid viscosity, Down-hole NMR system, Crude oil
09
2014


Abstract:
Pore length scales and pore surface relaxivities of rock cores with different lithologies were studied on a 2<ce:hsp sp="0.25"/>MHz Rock Core Analyzer. To determine the pore length scales of the rock cores, the high eigenmodes of spin bearing molecules satisfying the diffusion equation were detected with optimized encoding periods in the presence of internal magnetic fields B in . The results were confirmed using a 64<ce:hsp sp="0.25"/>MHz NMR system, which supports the feasibility of high eigenmode detection at fields as low as 2<ce:hsp sp="0.25"/>MHz. Furthermore, this methodology was combined with relaxometry measurements to a two-dimensional experiment, which provides correlation between pore length and relaxation time. This techniques also yields information on the surface relaxivity of the rock cores. The estimated surface relaxivities were then compared to the results using an independent NMR method.
Keywords: Low-field NMR, Pore length scales, Pore surface relaxivity
09
2014


Abstract:
Pore length scales and pore surface relaxivities of rock cores with different lithologies were studied on a 2 MHz Rock Core Analyzer. To determine the pore length scales of the rock cores, the high eigenmodes of spin bearing molecules satisfying the diffusion equation were detected with optimized encoding periods in the presence of internal magnetic fields Bin. The results were confirmed using a 64 MHz NMR system, which supports the feasibility of high eigenmode detection at fields as low as 2 MHz. Furthermore, this methodology was combined with relaxometry measurements to a two-dimensional experiment, which provides correlation between pore length and relaxation time. This techniques also yields information on the surface relaxivity of the rock cores. The estimated surface relaxivities were then compared to the results using an independent NMR method.
Keywords: Low-field NMR, Pore length scales, Pore surface relaxivity
09
2014


Abstract:
Internal magnetic gradient plays a significant role in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) measurements of fluid saturated porous media. The quantitative characterization and application of this physical phenomenon could effectively improve the accuracy of NMR measurements and interpretations. In this paper, by using the equivalent magnetic dipole method, the three-dimensional distribution of internal induced magnetic field and its gradients in the randomly packed water saturated glass beads are quantitatively characterized. By simulating the diffusive motion of water molecules in porous media with random walk method, the computational dephasing effects equation related to internal gradients is deduced. Thereafter, the echo amplitudes are obtained and the corresponding T 2-G spectrum is also inverted. For the sake of verifying the simulation results, an experiment is carried out using the Halbach core analyzing system (B 0=0.18 T, G=2.3 T/m) to detect the induced internal field and gradients. The simulation results indicate the equivalent internal gradient is a distribution of 0.12–0.3 T/m, which matched well with the experimental results.
Keywords: porous media, NMR, internal gradients, dephasing effect, inhomogeneous field
摘要:
在饱和多相流体孔隙介质中,利用核磁共振测得的扩散系数可以区分油气水,并用于饱和度等岩石物理参数的求取,但在微小孔隙(<20μm)中,流体的表观扩散系数会偏离其自由扩散系数.通过有限差分和随机游走模拟方法对水分子在单孔隙及多孔隙介质中的扩散进行数值模拟,考察水分子扩散受限的程度.结合核磁共振在测井及实验室岩石物理应用的技术,进一步分析了受限扩散对求取油水饱和度等岩石物理参数造成的影响.同时,分析总结了两种模拟方法的使用条件及优缺点.
关键词:核磁共振(NMR), 受限扩散, 微小孔隙, 有限差分, 随机游走
11
2013


Abstract:
A fast inverse Laplace transform (ILT) for the three-dimensional (3-D) nuclear magnetic resonance distribution was proposed by the authors with a designed pulse sequence and an efficient data-processing algorithm in Zhang et al. (Appl Magn Reson 44:849–857, 2013). In this paper, evaluation method to the 3-D ILT algorithm is introduced and the simulation results using simulated data with three different signal-to-noise ratios demonstrate that the precision and speed are excellent.
Keywords: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Residual Error, Inversion Result, Inverse Laplace Transform, Laplace Inversion
09
2013


Abstract:
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) under motion has drawn significant attention in recent years. Motion of the NMR probe has serious effects on NMR measurement. For example, NMR logging normally runs at downhole condition with tool motion at a speed of 30 ft/min. We propose here methods for motion corrections of NMR data based on the quantitative analysis of motion effects on polarization and echo acquisition. We also produced a multi-functional NMR scanning system to verify the theoretical analysis. Presented experiments demonstrate that the theoretical and experimental results match very well.
Keywords: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Vertical Resolution, Magnetization Vector, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Signal
09
2013


Abstract:
Heavy oil is a complicated mixture and a potential resource and has attracted much attention since the end of last century. It is important to characterize the composition of heavy oil to enhance its recovery efficiency. A designed unilateral Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) sensor with a Larmor frequency of 20 MHz and a well-defined constant gradient of 23.25 T/m was employed to acquire three-dimensional (3D) data for three heavy oil samples. The highly-constant gradient is advantageous for diffusion coefficient measurement of heavy oil. A fast data-implementation procedure including specially designed 3D pulse sequence and Inversion Laplace Transform (ILT) algorithm was adopted to process the data and extract 3D T1D-T2 probability function. It indicates that NMR relaxometry and diffusometry are useful to characterize the components of heavy oil samples. NMR results were compared with independent measurements of fractionation and gas chromatography analysis.
Key words:Heavy oil, multi-dimensional NMR, unilateral sensor
摘要:
能够反映孔隙介质内部真实复杂结构的CT图像经常被用于模拟研究中并能取得较好的结果.但是,在很多情况下缺少三维CT图像或者其分辨率受限,此时,更易于获取的二维薄片图像被用于构建三维的孔隙结构图像.假定孔隙介质各向同性,基于二维图像,使用多点统计方法可以构建岩石的三维孔隙结构.基于数字图像,采用随机游走方法模拟得到核磁共振响应,然后由模拟得到的回波串反演得到丁2分布.研究表明,岩石重构图像中的模拟结果与CT图像中的模拟结果有较好的一致性.基于数字图像的核磁共振响应模拟为分析不同孔隙结构的核磁共振响应提供了便利,同时,模拟结果也为验证孔隙结构的重构效果提供了依据.
关键词:核磁共振(NMR), 数字图像, 随机游走, 多孔介质, 多点统计, 重构
摘要:
随钻核磁共振测井的地层界面响应特征对地质导向和原状地层评价具有重要意义,但钻井轨迹的复杂性决定其响应特征是多重因素综合作用的结果,且较难直接给出统一显式表达式.本文根据仪器在地层内的运动特征,建立了基于敏感区域体积元的随钻核磁共振测井响应方程和离散化计算方法;通过正演、反演结合的数值模拟,研究了单、双界面水平层状地层中,不同井斜角度、天线长度和目标地层厚度等条件下的随钻核磁共振测井响应特征,对关键结果给出了成立条件和定量关系.随钻核磁共振测井在斜井段中的T2分布和孔隙度响应与直井中差异明显;井斜角越大,视地层厚度越大,地层界面在T2分布和孔隙度曲线上的过渡段越长,T2分布过渡起始位置已不能确定界面深度;仪器的最高纵向分辨率与天线长度、井眼条件和仪器参数有关;受围岩作用影响,较薄目的层的测井响应特征上可能出现异常"夹层".基于分析结果,对随钻核磁共振测井资料解释提出了建议.
关键词:随钻核磁共振测井 地层界面 响应特征 大斜度与水平井
07
2013


Abstract:
Three-dimensional (3-D) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments reflect material structure, such as physical array of porous media and chemical compositions of complex fluids. However, a huge database is acquired in multi-dimensional NMR and obstructs the extraction of this information in a proper manner. In this paper, a new fast 3-D Laplace inversion procedure is introduced which contains a specially designed 3-D pulse sequence to acquire the data responding to interesting NMR properties simultaneously and efficient data-processing algorithm referring this pulse sequence. A 3-D NMR experiment in low-field on water-saturated synthetic porous sample is presented to demonstrate the validity of the designed 3-D inverse Laplace algorithm.
Keywords:Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Singular Value Decomposition, Glass Bead, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiment, Inverse Laplace Transformation
摘要:
研制一种新型低场核磁共振孔隙介质分析仪,通过对不同直径岩样的实际测量,可以快速提供含流体孔隙介质的T2分布,T1分布,T1-T2和D-T2二维分布等重要信息,证实了仪器的合理性,有效性,及便捷性。采用Hal-bach磁体和可变尺寸开槽法拉第屏蔽螺线管天线,方便了样品制备和探测效率。低成本线性功率放大器的输出功率可达250 W,能够满足线圈激励要求,并降低成本。有源场效应管组成的隔离电路工作频率较宽,具有通用性。射频三极管组成的负反馈放大电路作为前置放大电路的第一级保证接收回路的低噪声设计,三极管集电极电流由运放为核心的虚拟电流源,使电路设计简化。DSP和FPGA作为主控电路的运算和逻辑控制单元,使回波信号提取和脉冲序列时序生成更灵活。
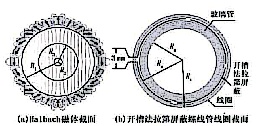
关键词: 核磁共振分析仪, 低场, 孔隙介质, Halbach磁体,探测效率
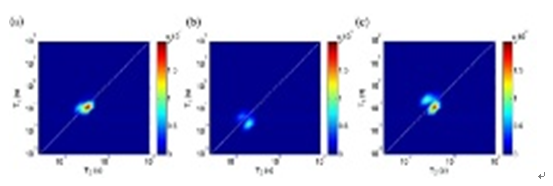
06
2013


Abstract:
Multi-dimensional NMR experiments at two magnetic field strengths (2 and 23 MHz) are presented in this paper to study the dependence of effective internal gradients in water-saturated sandstone plugs. Special pulse sequence is designed to encode longitudinal relaxation time T1, internal gradient Gin and transverse relaxation time T2 in respective windows. Experimental three-dimensional data are processed with a fast 3D inversion algorithm. Within this one-shot experiment, the three-dimensional distribution function T1-Gin-T2 and projected one- and two-dimensional distributions monitor internal gradients through diffusion in pores and reveal how effective internal gradients scale with magnetic field. Contrasts in behavior of pore size components between the two field strengths, such as T1/T2 ratio increase in T2–T1 maps and signal up-shift in T1-Gin and T2-Gin maps, are associated with variations in effective internal gradients in porous media, so potentially indicating the physical dependence of internal gradients on static field strengths and on heterogeneity of the sandstone matrix.
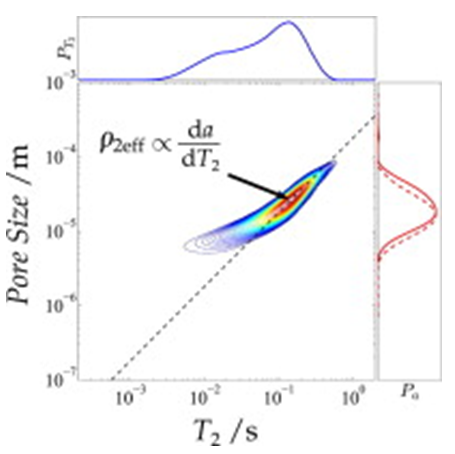
Keywords:Internal gradients, Sandstone, Multi-dimensional NMR
摘要:
缩短射频脉冲宽度,有助于解决脉冲电力消耗大、样品吸收率高、信噪比低等极端条件核磁共振探测的关键问题.本文首先分析射频脉冲角度对核磁共振自旋回波信号强度的影响机理,基于Bloch方程推导了回波信号幅度与扳转角、重聚角的关系.在特制核磁共振分析仪上采用变脉冲角度技术,分别在均匀磁场和梯度磁场条件下实现对扳转角和重聚角与回波信号强度关系的数值模拟和实验测量.结果表明,梯度场中,扳转角为90°、重聚角为140°的射频脉冲组合获得最大首波信号强度,比180°脉冲对应的回波幅值提高13%,能耗降低至78%.选用该重聚角(140°)优化设计饱和恢复脉冲序列探测流体的纵向弛豫时间T1特性,准确获得T1分布.该结果对于低电力供应、且对信噪比有较高要求的核磁共振测量,如随钻核磁共振测井和在线核磁共振快速检测等,具有重要意义.
关键词: 核磁共振, 信号强度, 重聚脉冲角度, Bloch方程
05
2013


Abstract:
Combination of two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (2-D NMR) correlation maps and a simple three-component model are proposed here to identify the structural composition of porous media. Homogeneous magnetic field and field with constant gradient of a novel Halbach sensor are employed for respective relaxation and diffusion measurements. NMR results are compared and confirmed with independent measurements on a scanning electron microscope and by energy dispersive spectrometer methods.
Keywords:Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiment, Structural Composition, Pulse Field Gradient
01
2014


Internal magnetic gradient plays a significant role in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance(NMR)measurements of fluid saturated porous media.The quantitative characterization and application of this physical phenomenon could effectively improve the accuracy of NMR measurements and interpretations.In this paper,by using the equivalent magnetic dipole method,the three-dimensional distribution of internal induced magnetic field and its gradients in the randomly packed water saturated glass beads are quantitatively characterized.By simulating the diffusive motion of water molecules in porous media with random walk method,the computational dephasing effects equation related to internal gradients is deduced.
关键词porous media,NMR,internal gradients,dephasing effect,inhomogeneous field
09
2013


摘要:Heavy oil is a complicated mixture and a potential resource and has attracted much attention since the end of last century. It is important to characterize the composition of heavy oil to enhance its recovery efficiency. A designed unilateral Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) sensor with a Larmor frequency of 20 MHz and a well-defined constant gradient of 23.25 T/m was employed to acquire three-dimensional (3D) data for three heavy oil samples.
01
2013


Abstract
Multi-dimensional NMR experiments at two magnetic field strengths (2 and 23 MHz) are presented in this paper to study the dependence of effective internal gradients in water-saturated sandstone plugs. Special pulse sequence is designed to encode longitudinal relaxation time T1, internal gradient Gin and transverse relaxation time T2 in respective windows. Experimental three-dimensional data are processed with a fast 3D inversion algorithm. Within this one-shot experiment, the three-dimensional distribution function T1-Gin-T2 and projected one- and two-dimensional distributions monitor internal gradients through diffusion in pores and reveal how effective internal gradients scale with magnetic field. Contrasts in behavior of pore size components between the two field strengths, such as T1/T2 ratio increase in T2–T1 maps and signal up-shift in T1-Gin and T2-Gin maps, are associated with variations in effective internal gradients in porous media, so potentially indicating the physical dependence of internal gradients on static field strengths and on heterogeneity of the sandstone matrix.

Keywords
Internal gradients
Sandstone
Multi-dimensional NMR
摘要:设计了一种用于核磁共振测井仪的低噪声模拟接收电路。第1级放大为自主构建的仪器用放大器,其增益为52dB,选用最佳源电阻与天线谐振阻抗相近的超低噪声宽带运放LMH6626保证电路的低噪声性能。对第1级放大器的噪声性能进行了理论分析,其噪声系数为1.45。实验测试结果表明,电路最大增益为112dB,频率范围为400kHz~1MHz,可对核磁共振信号进行低噪声放大,并已成功应用于核磁共振测井仪实验室样机中。
关键词: 核磁共振测井仪;低噪声;模拟接收电路;放大器;噪声性能;电路设计;
摘要:研制一种新型低场核磁共振孔隙介质分析仪,通过对不同直径岩样的实际测量,可以快速提供含流体孔隙介质的T2分布,T1分布,T1-T2和D-T2二维分布等重要信息,证实了仪器的合理性,有效性,及便捷性。采用Hal-bach磁体和可变尺寸开槽法拉第屏蔽螺线管天线,方便了样品制备和探测效率。低成本线性功率放大器的输出功率可达250 W,能够满足线圈激励要求,并降低成本。有源场效应管组成的隔离电路工作频率较宽,具有通用性。射频三极管组成的负反馈放大电路作为前置放大电路的第一级保证接收回路的低噪声设计,三极管集电极电流由运放为核心的虚拟电流源,使电路设计简化。DSP和FPGA作为主控电路的运算和逻辑控制单元,使回波信号提取和脉冲序列时序生成更灵活。
关键词: 核磁共振分析仪;低场;孔隙介质;Halbach磁体;探测效率;
摘要:缩短射频脉冲宽度,有助于解决脉冲电力消耗大、样品吸收率高、信噪比低等极端条件核磁共振探测的关键问题.本文首先分析射频脉冲角度对核磁共振自旋回波信号强度的影响机理,基于Bloch方程推导了回波信号幅度与扳转角、重聚角的关系.在特制核磁共振分析仪上采用变脉冲角度技术,分别在均匀磁场和梯度磁场条件下实现对扳转角和重聚角与回波信号强度关系的数值模拟和实验测量.结果表明,梯度场中,扳转角为90°、重聚角为140°的射频脉冲组合获得最大首波信号强度,比180°脉冲对应的回波幅值提高13%,能耗降低至78%.选用该重聚角(140°)优化设计饱和恢复脉冲序列探测流体的纵向弛豫时间T1特性,准确获得T1分布.该结果对于低电力供应、且对信噪比有较高要求的核磁共振测量,如随钻核磁共振测井和在线核磁共振快速检测等,具有重要意义.
关键词: 核磁共振;信号强度;重聚脉冲角度;Bloch方程;
摘要:核磁共振(NMR)测井是在高温、高压的极端条件下进行,样品体积小,回波幅度微弱.受到来源复杂的噪声影响,NMR信号通常被淹没在噪声中,测量数据的信噪比较低.提出正则化-启发式阈值算法(Regularization Heursure,R-Heursure)对小波分解后的细节系数阈值降噪,正则化因子的选取与地层孔隙结构和测量数据的原始信噪比相关.通过最大相关系数能量准则选取最优化的母小波函数、消失矩和分解层次,采用正则化因子约束估计的阈值,使选取的阈值恰好能大于噪声水平而不损失小孔(或微孔)的响应信息.数值模拟和实际测井资料处理验证了R-Heursure算法的降噪性能,NMR测井数据的信噪比得以有效改善,为储层评价提供更准确的信息.
关键词: 正则化-启发式阈值;核磁共振测井;回波串降噪;小波变换;
摘要:随钻核磁共振测井的地层界面响应特征对地质导向和原状地层评价具有重要意义,但钻井轨迹的复杂性决定其响应特征是多重因素综合作用的结果,且较难直接给出统一显式表达式.本文根据仪器在地层内的运动特征,建立了基于敏感区域体积元的随钻核磁共振测井响应方程和离散化计算方法;通过正演、反演结合的数值模拟,研究了单、双界面水平层状地层中,不同井斜角度、天线长度和目标地层厚度等条件下的随钻核磁共振测井响应特征,对关键结果给出了成立条件和定量关系.随钻核磁共振测井在斜井段中的T2分布和孔隙度响应与直井中差异明显;井斜角越大,视地层厚度越大,地层界面在T2分布和孔隙度曲线上的过渡段越长,T2分布过渡起始位置已不能确定界面深度;仪器的最高纵向分辨率与天线长度、井眼条件和仪器参数有关;受围岩作用影响,较薄目的层的测井响应特征上可能出现异常"夹层".基于分析结果,对随钻核磁共振测井资料解释提出了建议.
关键词: 随钻核磁共振测井;地层界面;响应特征;大斜度与水平井;
摘要:
仪器在运动的状态下对被测样品进行核磁共振(NMR)测量是一种新的测量方式,这不但可以提高测量效率,而且可以实现对样品的分层结构、夹层及裂缝的分布信息的在线监测。
摘要:核磁共振(NMR)测井仪以CPMG脉冲序列为测量基础,按照CPMG脉冲序列的时序要求完成大功率射频脉冲的发射和微弱回波信号的接收,在脉冲发射完成后快速泄放天线中储存的能量.该文介绍一种基于现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)的NMR测井仪控制逻辑和典型脉冲序列,详细说明在CPMG脉冲序列下FPGA的工作时序和流程;讨论NMR测井仪发射电路、Q-转换电路和隔离电路的控制原理和时序要求,给出各电路的控制逻辑仿真结果;最后,利用所设计的控制逻辑和自制NMR测井仪探头,在实验室条件下对水溶液进行了测量,得到满意的结果.
关键词: 核磁共振测井仪;CPMG;脉冲序列;FPGA;
摘要:核磁共振测井仪探头的优化设计能够增强仪器的探测特性,提高仪器的信噪比,而探头设计中的数值方法对设计结果至关重要.本文利用电磁场有限元方法对贴井壁型核磁共振测井仪探头静磁场和射频场进行了2D和3D的数值模拟,深入分析了数值模型形状、模型尺寸、单元形状对数值模拟结果的影响,并将有限元数值模拟结果与实测数据做了对比.结果显示:数值模拟结果与实测数据符合.在设计核磁共振测井仪探头结构时,选取与井眼形状一致的圆形模型,模型尺寸范围在10—15倍探头外径,并采用三角形单元可以有效提高数值模拟方法精度,增强优化设计结果的可靠性.
关键词: 核磁共振测井;探头设计;有限元;磁场分布;
摘要:饱和流体孔隙介质中存在的内部磁场梯度会对孔隙介质的核磁共振产生显著影响,提出了一种基于(T2int,D)二维核磁共振方法计算饱和多相流体孔隙介质内部磁场梯度的方法,可以计算饱和水以及油水多相流体的孔隙介质中内部磁场梯度.数值模拟与实验测量表明,该方法计算的饱和流体孔隙介质内部磁场梯度是有效的.
关键词: 多相流体;孔隙介质;二维核磁共振;内部磁场梯度;
摘要:
磁化系数是一种重要的物理性质,可用于表征物质材料中的特殊元素含量和被磁化的难易程度。在自然或人造的孔隙介质中,由于固体骨架与饱含在孔隙空间内部的液体之间磁化系数存在差异,在孔隙中会形成一个与空间位置有关的内部梯度磁场。通过测量分析该场的分布与大小可用于研究物质磁化系数的差异。
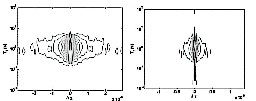
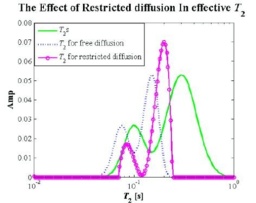
摘要:
受限扩散在微小孔隙中是一种常见现象,随扩散时间变化的视扩散系数能提供很多多孔介质的信息。在短扩散时间时,视扩散系数值的大小不依赖于孔隙形状的微小结构,而仅仅与孔隙空间的比表面比(S/V)有关,因此我们可以通过短时状态下的受限扩散去求取孔隙尺寸的大小,例如在球形孔隙中,直径d=6/。
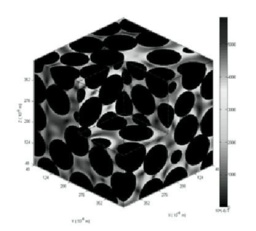
摘要:
粒子自旋散相效应的观测是孔隙介质中核磁共振响应信号采集与实现的物理基础。它是被测流体的物理特性、外加磁场强度、信号采集参数的综合表征。孔隙介质中固体骨架与饱和在其中的流体之间磁化系数的差异会引起与空间位置有关的内部感应磁场梯度,造成磁场的非均匀性。该特性会对孔隙介质中的粒子的自旋散相效应产生不可忽视的影响。
摘要:
核磁共振(NMR)测井仪以CPMG脉冲序列为测量基础,按照CPMG脉冲序列的时序要求完成大功率射频脉冲的发射和微弱回波信号的接收,在脉冲发射完成后快速泄放天线中储存的能量.该文介绍一种基于现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)的NMR测井仪控制逻辑和典型脉冲序列,详细说明在CPMG脉冲序列下FPGA的工作时序和流程;讨论NMR测井仪发射电路、Q转换电路和隔离电路的控制原理和时序要求,给出各电路的控制逻辑仿真结果;最后,利用所设计的控制逻辑和自制NMR测井仪探头,在实验室条件下对水溶液进行了测量,得到满意的结果.
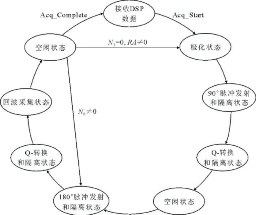
关键词:核磁共振测井仪, FPGA
摘要:介绍随钻核磁共振(NMR)测井的发展和现状。基于测量环境和工作方式,讨论运动中随钻核磁共振测井的特殊问题和探测特征。随钻NMR测井技术的关键在于其具有特殊探测特性的探头能够满足磁体尺寸受限、测量过程中仪器的复杂机械运动和电力供应等钻井条件下的特殊要求。随钻核磁共振测井与电缆核磁共振测井应用实例的对比分析说明随钻核磁共振测量技术是可靠的,在高成本、强实效的钻井作业中将发挥越来越重要的作用。我国的随钻NMR测井仪的研发过程应在消化吸收国外仪器方案的基础上探索分析探头设计方案并进行数值模拟和论证;对探头方案进行物理实现,建立钻井条件仿真装置验证探头关键技术;最优方案形成完整系统后进入实际验证。
关键词: 随钻测井;核磁共振测井;关键技术;探头;发展;
摘要:核磁共振产生的回波信号幅度比较低,容易受到噪声干扰.如何有效提高低场核磁共振回波信号的信噪比一直是核磁共振技术研究的关键课题之一.本文讨论了一种基于小波变换的Stein无偏风险估计(SURE)算法,从相关系数图版中确定尺度因子和分解层次,依据噪声在不同分解层次上的差异取不同的阈值对回波信号去噪.该算法与传统的模极大值法和空域相关法相比,能获得更高的信噪比,为储层流体分析提供更准确的孔隙度信息.
关键词: 核磁共振;回波去噪;SURE;SVD反演;小波变换;
摘要:介绍随钻核磁共振(NMR)测井的发展和现状。基于测量环境和工作方式,讨论运动中随钻核磁共振测井的特殊问题和探测特征。随钻NMR测井技术的关键在于其具有特殊探测特性的探头能够满足磁体尺寸受限、测量过程中仪器的复杂机械运动和电力供应等钻井条件下的特殊要求。随钻核磁共振测井与电缆核磁共振测井应用实例的对比分析说明随钻核磁共振测量技术是可靠的,在高成本、强实效的钻井作业中将发挥越来越重要的作用。我国的随钻NMR测井仪的研发过程应在消化吸收国外仪器方案的基础上探索分析探头设计方案并进行数值模拟和论证;对探头方案进行物理实现,建立钻井条件仿真装置验证探头关键技术;最优方案形成完整系统后进入实际验证。
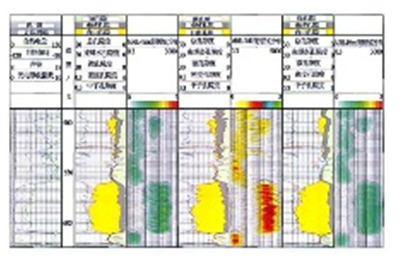
关键词: 随钻测井, 核磁共振测井, 关键技术, 探头, 发展
01
2009


摘要:提出一种核磁共振多回波串数据联合反演方法,分别对核磁共振孔隙度测量的两组回波串数据、变等待时间多回波串数据以及变回波间隔多回波串数据进行了处理.结果表明,这样处理得到的一维核磁共振T2分布不但连续,而且能够揭示短横向弛豫组分的细微特征,提高了核磁共振孔隙度的精度.处理变等待时间或变回波间隔下的多回波串数据,可以得到孔隙流体的(T2,T1)或(T2,D)二维核磁共振分布图.与一维核磁共振T2分布相比,二维核磁共振提高了识别流体的效果.
关键词: 核磁共振;测井;数据反演;孔隙度;流体识别;
摘要:研究气层在欠平衡和超平衡测井条件下响应特征的差异,对于欠平衡条件下天然气储层的评价和测井资料的应用具有指导意义.利用Monte Carlo数值模拟技术,计算得到了在欠平衡和超平衡测井条件下,补偿中子和密度测井随井眼直径、地层孔隙度和含气饱和度的变化关系.从而得出,在井眼直径较小时,密度和中子测井,在超平衡测井或欠平衡测井条件下,对气层的响应特征基本相同,欠平衡密度测井资料可以正常应用,不需要做校正处理;当井眼直径较大时,井内介质对探测器的影响不同,需要对欠平衡测井资料做井径的影响校正.
关键词: 欠平衡测井;密度测井;中子测井;气层;响应;
摘要:孔隙度是评价储层的基本参数,核磁共振测井是确定储层孔隙度的有效方法.但是,实践中也发现复杂流体储层核磁共振测井孔隙度与地层实际孔隙度存在较大差异,影响了核磁共振测井的应用效果.根据含复杂流体储层的核磁共振测井孔隙度响应方程,分别从流体的纵向弛豫时间、横向弛豫时间、含氢指数以及井眼环境等方面系统研究了影响核磁共振测井孔隙度的各种因素,给出了各因素的影响规律及校正方法,为提高复杂流体储层核磁共振测井孔隙度的应用效果以及发展适合陆相地层核磁共振孔隙度测量方法提供理论基础与实验依据.
关键词: 核磁共振测井;复杂流体储层;孔隙度;影响因素;
摘要:温度是影响核磁共振弛豫的一个因素。目前国内各实验室所做的核磁共振实验测量大都局限在室温下,实验温度与地下储集层温度有很大差别,因此有必要研究温度对流体及饱和流体岩石的核磁共振弛豫的影响,提高核磁共振测井资料评价精度。本文选取自由水、不同粘度脱气原油、饱和水以及饱和变压器油的储层贝瑞砂岩和储层碳酸盐岩样品进行核磁共振变温实验,测量温度从25℃变化到90℃。结果表明:自由水和原油的核磁共振横向弛豫时间(T2)都随温度的升高而增大。温度对饱和水贝瑞砂岩和碳酸盐岩核磁共振弛豫的影响不同,饱和水贝瑞砂岩核磁共振横向弛豫时间随温度升高而减小,而饱和水碳酸盐岩横向弛豫时间随温度升高而增大。无论是饱和油的贝瑞砂岩或是饱和油的碳酸盐岩,其核磁共振横向弛豫时间都随温度升高而增大。温度对核磁共振弛豫的影响,会造成室温下得到的横向弛豫时间截止值(T2cutoff)与储层温度下的实际值有偏差,影响储层束缚水饱和度和渗透率的计算结果,建议在核磁共振测井资料解释及应用时应考虑温度的影响。
关键词: 核磁共振;横向弛豫时间;实验测量;温度特性;自由流体;饱和流体岩石;
摘要:孔隙介质核磁共振(NMR)弛豫信号的多指数反演在NMR岩芯分析与测井解释中起着关键作用.为了在不同信噪比条件下快速反演出高分辨率的弛豫时间谱,本文利用NMR正演模拟信号以及实验室NMR岩芯分析数据,研究横向弛豫时间布点数、原始回波采集个数、时间域数据压缩方式等对反演结果的影响.同时,在不同信噪比(SNR)下对不同的反演算法(SVD、BRD、SIRT)进行比较,考察反演算法对信噪比的敏感程度,并讨论了相应的校正方法.另外,还分析了信噪比对长、短弛豫组分的影响.研究表明在充分采集有用回波的情况下,减少回波个数,反演得到的弛豫时间谱趋向发散;增加布点数可以提高分辨率,但是需要更多的计算时间;时间域数据压缩可以加快反演计算速度;不同算法对信噪比的敏感程度不同,发展相应的校正方法可以提高反演质量.
关键词: 核磁共振测井;横向弛豫时间;正演模拟;多指数反演;影响因素;
摘要:孔隙度是储层评价的重要参数之一.核磁共振(NMR)孔隙度只对孔隙流体有响应,在确定地层孔隙度方面具有其他测井方法无法比拟的优势.但是,在中国陆相复杂地层的应用中常常发现NMR孔隙度与地层实际孔隙度存在差异,有时差异甚至很明显,影响了NMR测井的应用效果.介绍了NMR孔隙度的理论基础,在对NMR孔隙度影响因素分析的基础上,重点考察了国内现有的NMR孔隙度测井方法对测量结果的影响,通过对大量人造岩样和不同岩性的天然岩样的实验测量,提出了适合中国陆相地层的孔隙度测井方法,改善了NMR孔隙度的测量效果.针对中国陆相地层的复杂性,建议不同地区应根据具体情况进行岩心分析,确定恰当的NMR测井方法,以获得比较准确的NMR孔隙度.
关键词: NMR测井;陆相地层;孔隙度;
摘要:提出一种新的基于整体迭代修正的核磁共振(NMR)驰豫信号多指数反演方法,并对新方法的具体实现过程和应用效果进行了详细讨论。通过算例,对新方法和基于奇异值分解的MAP-Ⅱ算法反演结果进行了对比,分别给出不同布点方式以及不同信噪比下NMR横向和纵向弛豫信号的多指数反演结果。结果表明,在16~64点对数均匀布点时,新方法明显优于MAP-Ⅱ,特别是在信噪比较低的情况下,仍然能保证弛豫谱的真实性,该方法可应用于岩心NMR实验分析以及NMR测井资料解释处理。
关键词: 核磁共振;反演;算法;岩心分析;测井;
Copyright © 2021 北京青檬艾柯科技有限公司 版权所有 京ICP备2021013551号